API Traffic Control
Request Throttling
Introduction
Tyk’s Request Throttling feature provides a mechanism to manage traffic spikes by queuing and automatically retrying client requests that exceed rate limits, rather than immediately rejecting them. This helps protect upstream services from sudden bursts and improves the resilience of API interactions during temporary congestion.Quick Start
Overview
In this tutorial, we will configure Request Throttling on a Tyk Security Policy to protect a backend service from sudden traffic spikes. We’ll start by defining a basic rate limit on a policy, then enable throttling with specific retry settings to handle bursts exceeding that limit, associate a key with the policy, and finally test the behaviour using simulated traffic. This guide primarily uses the Tyk Dashboard for configuration.Prerequisites
- Working Tyk Environment: You need access to a running Tyk instance that includes both the Tyk Gateway and Tyk Dashboard components. For setup instructions using Docker, please refer to the Tyk Quick Start.
- Curl, seq and xargs: These tools will be used for testing.
Instructions
Create an API
-
Create an API:
- Log in to your Tyk Dashboard.
- Navigate to API Management > APIs
- Click Add New API
- Click Import
- Select Import Type as Tyk API
- Copy the below Tyk OAS definition in the text box and click Import API to create an API
Configure Policy and Rate Limit
2. Create and Configure an Security Policy with Rate Limiting: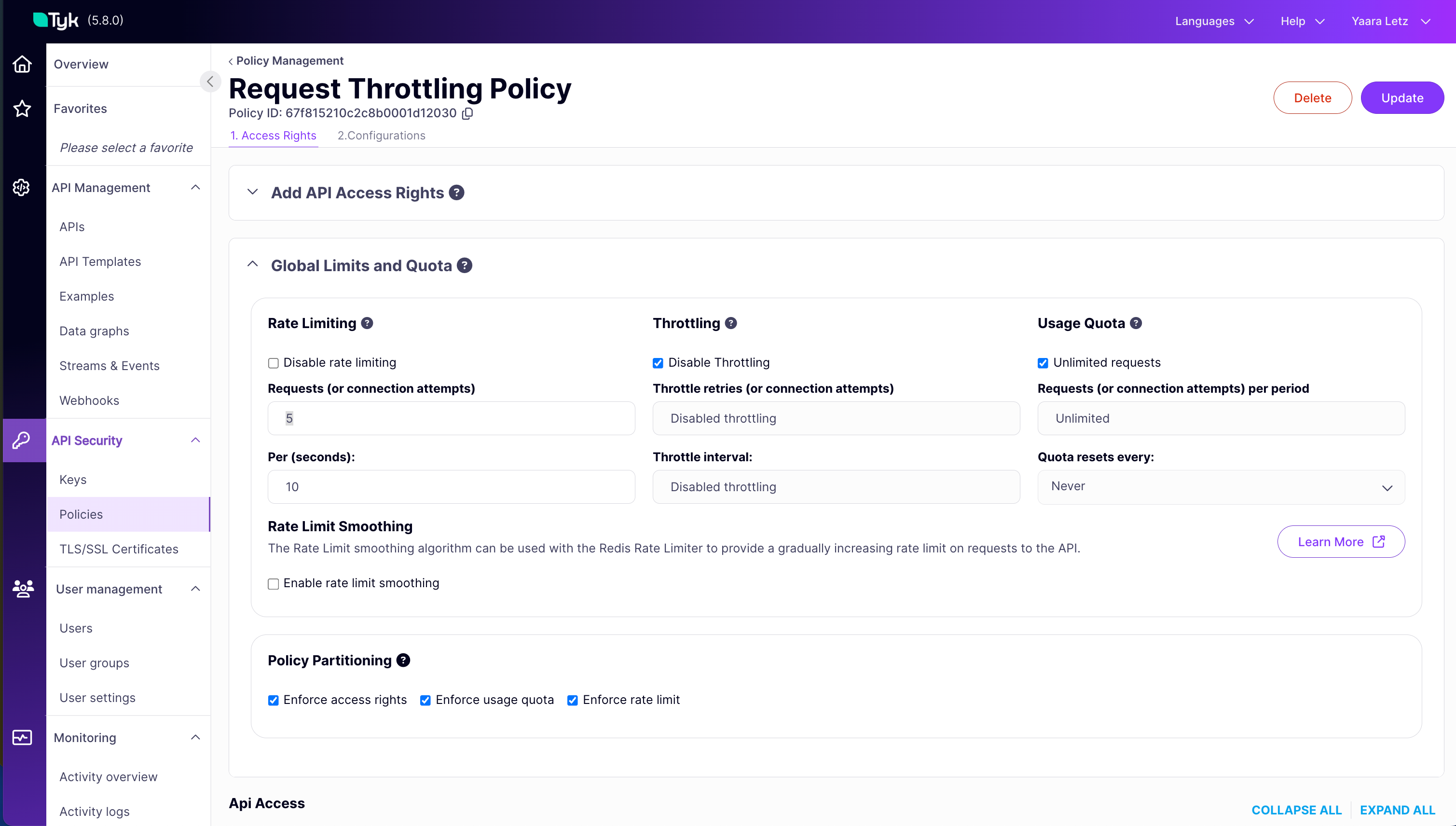
- Associate an Access Key with the Policy:
-
Test Rate Limit
So far, we’ve created a policy for an API definition and created a key that complies with that policy. Before enabling throttling, let’s observe the standard rate limiting behaviour. We’ll send 10 requests in parallel using
xargsto simulate a burst that exceeds our configured limit (5 requests per 10 seconds).- Open your terminal.
-
Execute the following command, replacing
<replace-with-key-id>with the API Key ID you saved earlier: -
Expected Observation: You should see some requests succeed with
HTTP/1.1 200 OK, and other requests failing withHTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requestsas the rate limit is immediately enforced. The order of200svs429smight vary depending upon the processing time, but you will see immediate rejections once the limit is hit.
Configure Throttling
Now that the policy enforces a basic rate limit, we will enable and configure Request Throttling. This adds the queue-and-retry behavior for requests that exceed the limit, preventing immediate rejection and helping to smooth out traffic spikes.-
Configure Request Throttling by Updating the Security Policy
- Navigate to API Security > Policies in the Tyk Dashboard sidebar
- Click on the
Request Throttling Policy - Under the 1. Access Rights tab:
- In the Global Limits and Quota section
- Set the following values for
Throttling - Uncheck the
Disable Throttlingcheckbox - Enter
3into the Throttle retries (or connection attempts) field - Enter
5into the Per (seconds): field
- Click the Update button
- A pop-up window will appear to confirm the changes. Click Update to close the pop-up
Testing
-
Test Request Throttling
-
Repeat the Test: Open your terminal and execute the exact same command as in step 4:
-
Expected Observation:
- You will still see the first ~5 requests return
HTTP/1.1 200 OKquickly - Critically, the subsequent requests (6 through 10) will not immediately return
429. Instead, you should observe a delay before their status lines appear - After the delay (
throttle_interval), Tyk will retry the queued requests. Some might now succeed (return200 OK) if the rate limit window allows - If a request is retried
throttle_retry_limit(3) times and still encounters the rate limit, then it will finally returnHTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests - Overall, you might see more
200 OKresponses compared to the previous test, and any429responses will appear significantly later
- You will still see the first ~5 requests return
(The exact mix of 200s and 429s on the delayed requests depends heavily on timing relative to the 10-second rate limit window reset and the retry attempts). -
Repeat the Test: Open your terminal and execute the exact same command as in step 4:
Configuration Options
Request Throttling is configured within Tyk Security Policies or directly on individual Access Keys. The configuration involves setting two specific fields:throttle_interval: Defines the wait time (in seconds) between retry attempts for a queued request. (Note: Do not set it to0. If you do, no delay is applied, and the request is immediately retried. This will creates a “busy waiting” scenario that consumes more resources than a positive interval value)throttle_retry_limit: Sets the maximum number of retry attempts before the request is rejected. (Note: Do not set it to0. Setting it to0means that there will be no throttling on the request)
0.
Disable throttling
The default value is-1 and means it is disabled by default.
Setting throttle_interval and throttle_retry_limit values to any number smaller than 0, to ensure the feature is diabled.
You can configure these settings using either the Tyk Dashboard UI or the Tyk Dashboard API.
Configure via UI
The Tyk Dashboard provides a straightforward interface to set throttling parameters on both Security Policies and Access Keys.The image below shows a policy with throttling. Any key using this policy will inherit the throttling settings and behaves as follows: wait 2 seconds between retries for queued requests, attempting up to 3 times before failing (so overall 6 seconds before getting another 429 error response).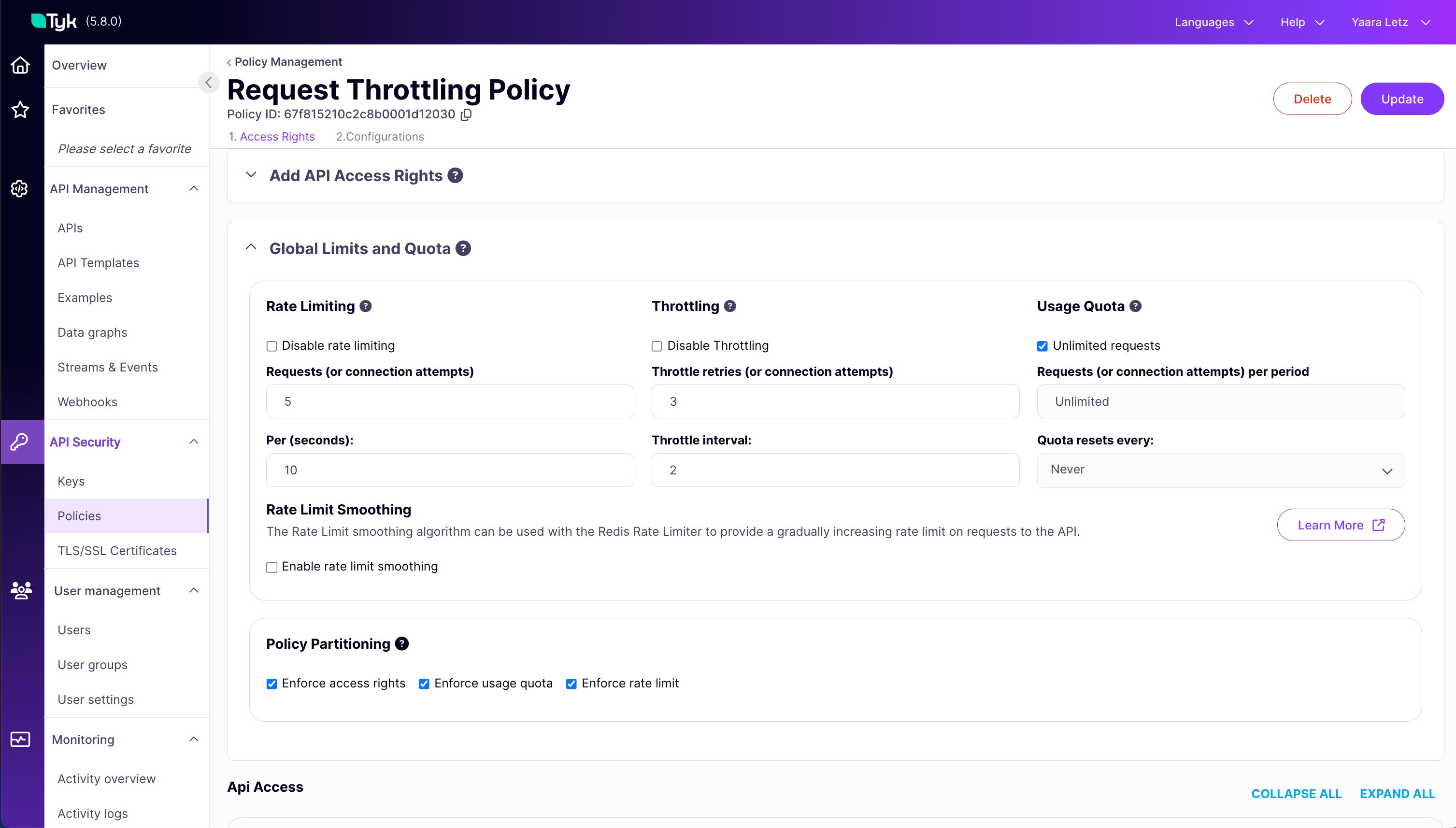

Configure via API
These are the fields that you can set directly in the Policy object or the Access Key:To update the policy, do the following:
- Retrieve the policy object using
GET /api/portal/policies/{POLICY_ID} - Add or modify the
throttle_intervalandthrottle_retry_limitfields within the policy JSON object - Update the policy using
PUT /api/portal/policies/{POLICY_ID}with the modified object, or create a new one usingPOST /api/portal/policies/
How It Works
Tyk’s Request Throttling intercepts API requests after they have exceeded a configured Rate Limit. Instead of immediately rejecting these requests with a429 Too Many Requests error (which is the default rate-limiting behaviour), the Gateway temporarily holds them in a queue. After waiting for a specified duration (throttle_interval), Tyk attempts to process the request again, re-checking the rate limit status.
This retry cycle repeats until either the request can be successfully processed (if capacity becomes available) or a configured maximum number of retries (throttle_retry_limit) is reached. Only after exhausting all retries does Tyk return the 429 error to the client.
Think of it like trying to access a service with a restriction on how many people can enter per minute (Rate Limit). If you arrive when the per-minute limit is full, standard behaviour is to turn you awa
y immediately. With Throttling enabled, the service instead asks you to wait briefly (the interval) and tries your entry again shortly, checking if the rate limit has freed up capacity, repeating this a f
ew times (the retry limit) before finally turning you away if access is still restricted.
FAQ
What is Request Throttling in Tyk?
What is Request Throttling in Tyk?
Request Throttling in Tyk is a mechanism that allows for graceful handling of rate limit violations. Instead of immediately rejecting requests that exceed rate limits, throttling gives clients a chance to retry after a specified delay.
How does Request Throttling differ from Rate Limiting?
How does Request Throttling differ from Rate Limiting?
Rate Limiting is a mechanism to restrict the number of requests a client can make in a given time period (e.g., 100 requests per minute). Request Throttling is an extension of rate limiting that provides a retry mechanism when rate limits are exceeded. Instead of immediately failing with a 429 status code, throttling allows the gateway to wait and retry the request internally.
Does Request Throttling work with Request Quotas?
Does Request Throttling work with Request Quotas?
No, Request Throttling in Tyk is exclusively linked to rate limits and does not work with request quotas. When a quota is exceeded, the request is immediately rejected without any throttling or retry attempts. Throttling is only applied when rate limits are exceeded.
How do I configure Request Throttling in Tyk?
How do I configure Request Throttling in Tyk?
Refer to this documentation.
How does Request Throttling affect response times?
How does Request Throttling affect response times?
Request Throttling can increase response times for requests that exceed rate limits, as the gateway will wait for the specified
ThrottleInterval between retry attempts. The maximum additional latency would be ThrottleInterval × ThrottleRetryLimit seconds. This trade-off provides better success rates at the cost of potentially longer response times for some requests.Can I monitor throttled requests in Tyk?
Can I monitor throttled requests in Tyk?
Yes, Tyk tracks throttled requests in its health check metrics. You can monitor the
ThrottledRequestsPS (throttled requests per second) metric to see how often requests are being throttled. Additionally, when a request is throttled, Tyk emits a RateLimitExceeded event that can be captured in your monitoring system.Is Request Throttling enabled by default?
Is Request Throttling enabled by default?
No, Request Throttling is not enabled by default. To enable throttling, you need to explicitly set
ThrottleRetryLimit to a value greater than 0 and configure an appropriate ThrottleInterval. These settings can be applied through policies or directly in access keys.
